Thanks to Anirudh for getting me started on the right path!
Running Signal Desktop in a Debian VM on OpenBSD
I wanted to get Signal Desktop running in a way that integrates smoothly with my OpenBSD host. Since Signal doesn’t have a native OpenBSD port, I spun up a Debian VM using vmm(4) and vmctl. Below are my notes for setting this up, including a few gotchas.
Step 1: Download Debian ISO
Start with the Bookworm Debian netinst ISO (I had issues with Trixie):
Step 2: Configure vmd Permissions
Allow your user account to control VMs by editing /etc/vm.conf:
socket owner :vmdusers
Step 3: Create Disk Image
vmctl create -s 40G debian.qcow2
Step 4: Configure Networking
Edit /etc/pf.conf and add:
match out on egress from 100.64.0.0/10 to any nat-to (egress)
pass in proto { udp tcp } from 100.64.0.0/10 to any port domain rdr-to 8.8.8.8 port domain
Reload pf:
doas pfctl -f /etc/pf.conf
Step 5: Boot and Install Debian
Start the VM:
vmctl start -c -m 2G -L -r debian.iso -d debian.qcow2
At boot, edit the installer line and replace quiet with:
console=ttyS0,115220n8
Install Debian with the usual defaults:
- Use the whole disk, single partition.
- Remove Gnome and only select SSH Server.
Reboot and update:
apt update && apt upgrade
Step 6: Install Basic Packages
apt install tmux sndiod sudo gpg libgl1-mesa-glx libcanberra-gtk-module
Enable sound:
systemctl enable sndiod
On the OpenBSD host:
doas rcctl set sndiod flags -L 0.0.0.0
Step 7: Install Signal
Follow the Signal Beta instructions (I use Beta because it supports the app tray in Gnome):
Signal Beta Desktop Install Guide
Step 8: SSH Config
Add an entry to ~/.ssh/config:
host debian
Hostname 100.64.1.3
User bob
Compression no
ForwardX11 yes
ServerAliveInterval 30
ServerAliveCountMax 10
Copy your SSH key to enable autologin.
Step 9: Signal Launch Script
Create ~/.bin/signal.sh:
#!/bin/sh
# signal: launch signal-desktop via a vm (vmm(4))
status="$(vmctl status debian | grep running)"
[[ "$status" == "" ]] && {
vmctl start debian
sleep 10
}
ssh -Y debian "export AUDIODEVICE=snd@100.64.2.2/0 && signal-desktop-beta &"> /dev/null
Make it executable:
chmod +x ~/.bin/signal.sh
Step 10: Autostart VM
Edit /etc/vm.conf:
socket owner :vmdusers
vm "debian" {
memory 4G
disk "/home/bob/vm/debian.qcow2"
local interface
owner bob
enable
}
Restart vmd:
doas rcctl restart vmd
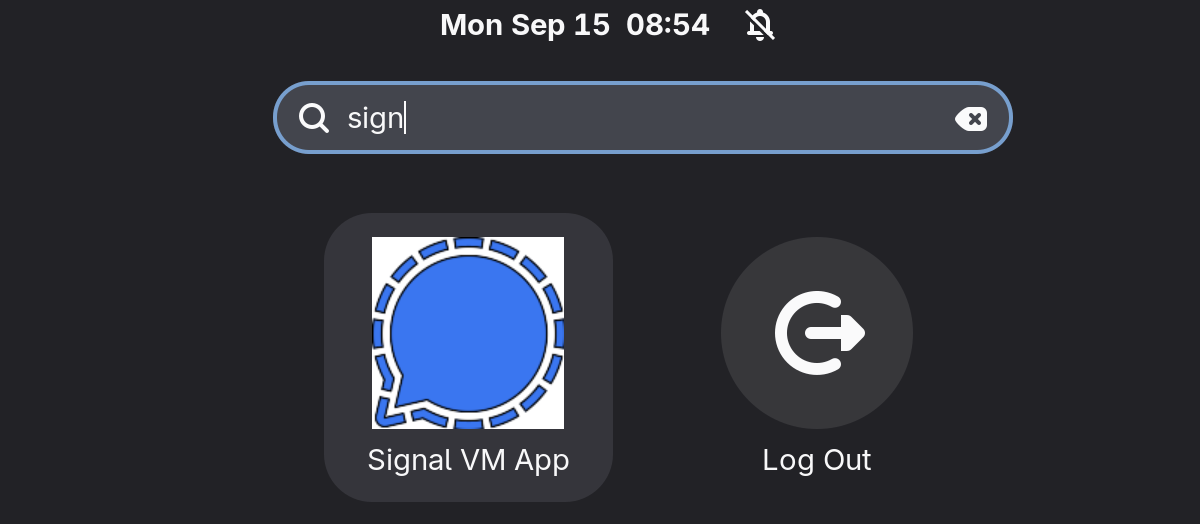
Step 11: Desktop Integration
Get an icon:
mkdir ~/.icons && cd ~/.icons
wget https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/4/41/Signal_ultramarine_icon.svg -O signal.svg
convert signal.svg signal.png
Create a desktop entry at ~/.local/share/applications/userapp-signal.desktop:
[Desktop Entry]
Version=1.0
Type=Application
Icon=/home/bob/.icons/signal.png
Exec=/home/bob/.bin/signal.sh
Name=Signal VM App
GenericName=Signal
Comment=Run the signal application from debian VM
X-Desktop-File-Install-Version=0.28
Install it:
desktop-file-install --dir=$HOME/.local/share/applications ~/.local/share/applications/userapp-signal.desktop
update-desktop-database ~/.local/share/applications
Gotchas
- I assume only one VM is running. If you run multiple VMs, the IP may change.
- Sound forwarding (
AUDIODEVICE) is not yet working for me, but the script is structured for consistency with other X11 applications. - I use Signal Desktop Beta as the app icon shows up in the tray. I have been unable to get the standard install to work and expose that.
- You could pick a weaker cipher for faster SSH connections with X11 Forwarding.
That’s it! You now have Signal Desktop running inside a Debian VM on OpenBSD, launched seamlessly from your desktop menu.